Worldwide Universal Healthcare Coverage


KEY FACTS
- 137 (58.8%) of countries have some form of universal healthcare system
- Europe has the highest number of countries with universal healthcare at 42 out of 48 countries (or 87.5%), followed by the Americas with 33 out of 53 countries (or 62.3%)
- Africa has the lowest number of countries with universal healthcare at 21 out of 57 countries (or 36.8%), followed by Oceania with 11 out of 24 countries (or 45.8%)
- In 2025, in terms of the universal healthcare coverage:
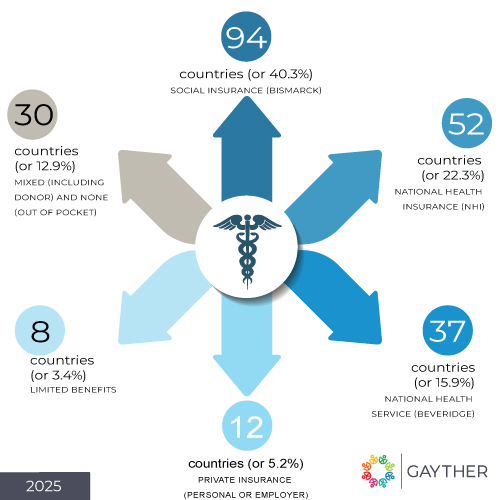
- Social Insurance (Bismarck) is the healthcare system most used in the world in 94 countries (or 40.3%), followed by National Health Insurance (NHI) in 52 countries (or 22.3%)
- National Health Service (Beveridge) is the healthcare system least used in the world in 37 countries (or 15.9%), a combination of private insurance, mixed, limited and none in 50 countries (or 21.5%)
- Europe has the highest number of countries with universal healthcare at 42 out of 48 countries (or 87.5%), followed by the Americas with 33 out of 53 countries (or 62.3%)
- Africa has the lowest number of countries with universal healthcare at 21 out of 57 countries (or 36.8%), followed by Oceania with 11 out of 24 countries (or 45.8%)
- Compared to the LGBTQIA+ Population Statistics:
- A combination of private insurance, mixed, limited and none equates to 28.5 million people (or 13.3%) of community members living in countries that offer limited or no universal healthcare benefits
- 185.8 million people (or 86.7%) live in countries that provide some form of benefits relating to universal healthcare
- Compared to the LGBTQIA+ Equality Index:
- 19.3 million people (or 9.0%) from the community live in countries that provide universal healthcare and score low or very low in terms of LGBTQIA+ equality
- 111.2 million people (or 51.9%) from the community live in countries that offer universal healthcare and score medium-high or medium-low in terms of LGBTQIA+ equality
- 28.6 million people (or 13.4%) from the community live in countries that provide universal healthcare and score high or very high in terms of LGBTQIA+ equality
- 55.2 million people (or 25.7%) from the community live in countries that do not offer any form of universal healthcare coverage
 Click on a specific country within the map to learn more about its healthcare structure and other health-related information
Click on a specific country within the map to learn more about its healthcare structure and other health-related information
The healthcare and pharmaceutical industry is one of the world’s largest and most important sectors. It is an industry responsible for keeping people across the globe healthy and maintaining, suppressing, or eradicating serious diseases and illnesses. There is likely not a person alive who has or will use some form of healthcare in the future. For many, it is a fundamental right within society and one of our basic needs. The industry is estimated to be over 1.4 trillion US dollars annually, and the costs and access to healthcare will vary depending on the country and its social welfare system.
Universal healthcare is the term used to describe access and availability of healthcare and whether a country covers some or all of the costs through taxation. Universal healthcare is comprised of three distinctive groups, the first relating to who is covered, the second what is and what is not covered, and the third relating to how the cost of any healthcare received is funded. There are three distinct universal healthcare models many countries follow and many more hybrid schemes.
Let us now look at the different classifications within healthcare, what each one means and the model they typically follow:
- None (Out of Pocket) means the country offers no universal healthcare. All costs for treatment and medication are to be paid directly and in full by the patient, with no financial support or aid from the government. Medical care and medications are often not regulated, so costs are typically higher for patients.
- Mixed model (inc donor) – is typically not considered universal healthcare as it is often not self-funded by the country. The country may have a limited system or may have had universal healthcare; however, the country will now likely be at war, rebuilding from a previous war, or suffering severe economic hardship such as droughts, resulting in medical facilities and costs being inaccessible and out of reach for ordinary citizens. The medical expenses and care will often be funded by other third-party countries, through the World Bank or organisations such as the United Nations and the World Health Organisation, as well as many charities such as MSF and the Red Cross.
- Limited Benefits – even though the country may offer citizens limited benefits, this category is not considered universal healthcare as the majority of the costs for treatment and medication will be paid directly and in part or in full by the patient.
- Private Insurance (Personal or Employer) – not considered universal healthcare and also known as the out-of-pocket model, private insurance means that citizens within any given country must obtain private medical insurance that covers any medical expenses that might occur. The insurance, obtained through an insurance company, will be purchased personally or through their employee. A regular contribution is made to the insurance provider in return for coverage, which may include specific conditions and exclusions. When an individual needs treatment, they will visit a hospital or general practitioner and some or all of the costs incurred are paid out through the insurance policy.
- Social Insurance (Bismarck) is part of the universal healthcare model. The model works whereby the insurance is funded jointly by the government and through the employers within that country who pay into sickness funds. Non-profit ventures typically manage the insurance, and most medical professionals and hospitals will operate privately. Social insurance will cover the patient’s care cost when an individual needs medical assistance.
- National Health Service (Beveridge) is part of the universal healthcare model whereby a country’s healthcare is effectively nationalised. The health authority will often own and operate all medical facilities and employ most medical professionals, with all fees for care and medication being provided free or heavily subsidised. The national health service is funded through taxation, in which those living within that country will contribute a portion of their income or on value-added services.
- National Health Insurance (NHI) is part of the universal healthcare model. The NHI combines the Bismark and Beveridge models, whereby every citizen in a country pays towards a national health insurance program. The government contributes partly through taxation and regulating the medical industry, ensuring treatment and medication costs are heavily reduced and controlled.
Though universal healthcare may exist in many countries, its quality, standard, and availability will often vary by region and authority. Whenever visiting a country different from yours, it is always advisable to take out adequate travel insurance to cover you should you have a medical emergency during your travels.
The universal healthcare classifications and groups have been collated using information from several sources and reports. Some countries on the list may have been incorrectly classified, or some services or benefits may have been withdrawn or changed over time. Though we endeavour to keep the worldwide universal healthcare coverage information up to date, we do not guarantee the accuracy or completion of any of the data presented. Wherever you travel, it is always advisable to carry out independent research before travelling to ensure you have the latest and most accurate information.

When reviewing data, it is crucial to understand what it represents, whether it reflects the world and the experience of all those affected. Changes within any given country or region are not restricted to a specific month of the year or even are automatically triggered. Change, especially concerning equality, gender recognition, same-sex marriages and the status of gay conversion therapy, often takes work. Typically by many large groups of dedicated and focused individuals advocating and fighting for justice for positive change within their local communities.
The indices have been created to help you understand the world around you; however, engaging with your global community is essential. It is vital, especially if you are familiar with your desired destination. By reaching out and communicating with other members of the LGBTQIA+ community, you can establish critical details. It only takes a small amount of effort in locating people from or those who have already visited your particular destination for advice. Engaging on social media and Gayther’s networking platform, Gayther Affinity, can help you connect with the global LGBTQIA+ community.
There are thousands of events taking place, it is not always easy to know what is going on and when, Gayther can help
Gayther...your community resource
Three dedicated websites offer various tools, services, guides, and much more. Free tools and services tailored toward all groups within the global LGBTQIA+ community
Discover more about the extensive tools, services and guides available on Gayther. From country and regional guides to LGBTQIA+ community resources, learn more about all that Gayther has to offer
- The index has been compiled and is correct as of June 8, 2025
- The index has been compiled using a variety of different sources, including news articles, publications and websites such as Wikipedia
IMPORTANT DISCLAIMER: The Worldwide Universal Healthcare Coverage guide has been compiled from various sources and websites. The information is based on the principal system that exists at a national level rather than for any given region, state or province. For some countries, whether there was limited or conflicting information regarding the healthcare system, the final entry would be based on consistent data and reasonable judgment. The Worldwide Universal Healthcare Coverage guide is for illustrative purposes only; we do not guarantee the accuracy or completeness of the data, and none of the information constitutes advice. It is essential that you carry out independent research on any countries you plan to visit before going, as information changes frequently. Your country’s foreign office will advise you on any given country’s status and whether it is safe to travel there. This page may contain external links to third party websites; Gayther provides these links for your convenience and does not endorse, warrant or recommend any particular products or services. By clicking on any external links, you will leave Gayther and be taken to the third-party website, which you do so at your own risk and by accessing the site, you will be required to comply with the external third party’s terms and conditions of use and privacy policies




















 AFGHANISTAN
AFGHANISTAN ALBANIA
ALBANIA ALGERIA
ALGERIA AMERICAN SAMOA
AMERICAN SAMOA ANDORRA
ANDORRA ANGOLA
ANGOLA ANGUILLA
ANGUILLA ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA
ANTIGUA AND BARBUDA ARGENTINA
ARGENTINA ARMENIA
ARMENIA AUSTRALIA
AUSTRALIA AUSTRIA
AUSTRIA AZERBAIJAN
AZERBAIJAN BAHAMAS, THE
BAHAMAS, THE BAHRAIN
BAHRAIN BANGLADESH
BANGLADESH BARBADOS
BARBADOS BELARUS
BELARUS BELGIUM
BELGIUM BELIZE
BELIZE BENIN
BENIN BERMUDA
BERMUDA BHUTAN
BHUTAN BOLIVIA
BOLIVIA BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA
BOSNIA AND HERZEGOVINA BOTSWANA
BOTSWANA BRAZIL
BRAZIL BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS
BRITISH VIRGIN ISLANDS BRUNEI DARUSSALAM
BRUNEI DARUSSALAM BULGARIA
BULGARIA BURKINA FASO
BURKINA FASO BURUNDI
BURUNDI CAMBODIA
CAMBODIA CAMEROON
CAMEROON CANADA
CANADA CAPE VERDE (CABO VERDE)
CAPE VERDE (CABO VERDE) CARIBBEAN NETHERLANDS
CARIBBEAN NETHERLANDS CAYMAN ISLANDS
CAYMAN ISLANDS CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC
CENTRAL AFRICAN REPUBLIC CHAD
CHAD CHANNEL ISLANDS
CHANNEL ISLANDS CHILE
CHILE CHINA
CHINA COLOMBIA
COLOMBIA COMOROS
COMOROS CONGO, D.REP
CONGO, D.REP CONGO, REP
CONGO, REP COOK ISLANDS
COOK ISLANDS COSTA RICA
COSTA RICA CROATIA
CROATIA CUBA
CUBA CYPRUS
CYPRUS CZECH REPUBLIC (CZECHIA)
CZECH REPUBLIC (CZECHIA) DENMARK
DENMARK DJIBOUTI
DJIBOUTI DOMINICA
DOMINICA DOMINICAN REPUBLIC
DOMINICAN REPUBLIC EAST TIMOR (TIMOR-LESTE)
EAST TIMOR (TIMOR-LESTE) ECUADOR
ECUADOR EGYPT
EGYPT EL SALVADOR
EL SALVADOR EQUATORIAL GUINEA
EQUATORIAL GUINEA ERITREA
ERITREA ESTONIA
ESTONIA ETHIOPIA
ETHIOPIA FALKLAND ISLANDS (LAS MALVINAS)
FALKLAND ISLANDS (LAS MALVINAS) FIJI
FIJI FINLAND
FINLAND FRANCE
FRANCE FRENCH GUIANA
FRENCH GUIANA FRENCH POLYNESIA
FRENCH POLYNESIA GABON
GABON GAMBIA, THE
GAMBIA, THE GEORGIA
GEORGIA GERMANY
GERMANY GHANA
GHANA GIBRALTAR
GIBRALTAR GREECE
GREECE GREENLAND
GREENLAND GRENADA
GRENADA GUADELOUPE
GUADELOUPE GUAM
GUAM GUATEMALA
GUATEMALA GUINEA
GUINEA GUINEA-BISSAU
GUINEA-BISSAU GUYANA
GUYANA HAITI
HAITI HONDURAS
HONDURAS HONG KONG
HONG KONG HUNGARY
HUNGARY ICELAND
ICELAND INDIA
INDIA INDONESIA
INDONESIA IRAN, ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF
IRAN, ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAQ
IRAQ IRELAND
IRELAND ISLE OF MAN
ISLE OF MAN ISRAEL
ISRAEL ITALY
ITALY IVORY COAST (COTE D’IVOIRE)
IVORY COAST (COTE D’IVOIRE) JAMAICA
JAMAICA JAPAN
JAPAN JORDAN
JORDAN KAZAKHSTAN
KAZAKHSTAN KENYA
KENYA KIRIBATI
KIRIBATI KOREA, NORTH (D.REP)
KOREA, NORTH (D.REP) KOREA, SOUTH (REP)
KOREA, SOUTH (REP) KOSOVO, REPUBLIC OF
KOSOVO, REPUBLIC OF KUWAIT
KUWAIT KYRGYZSTAN
KYRGYZSTAN LAOS
LAOS LATVIA
LATVIA LEBANON
LEBANON LESOTHO
LESOTHO LIBERIA
LIBERIA LIBYA
LIBYA LIECHTENSTEIN
LIECHTENSTEIN LITHUANIA
LITHUANIA LUXEMBOURG
LUXEMBOURG MACAU
MACAU MADAGASCAR
MADAGASCAR MALAWI
MALAWI MALAYSIA
MALAYSIA MALDIVES
MALDIVES MALI
MALI MALTA
MALTA MARSHALL ISLANDS
MARSHALL ISLANDS MARTINIQUE
MARTINIQUE MAURITANIA
MAURITANIA MAURITIUS
MAURITIUS MAYOTTE
MAYOTTE MEXICO
MEXICO MICRONESIA, F.S
MICRONESIA, F.S MOLDOVA
MOLDOVA MONACO
MONACO MONGOLIA
MONGOLIA MONTENEGRO
MONTENEGRO MOROCCO
MOROCCO MOZAMBIQUE
MOZAMBIQUE MYANMAR
MYANMAR NAMIBIA
NAMIBIA NAURU
NAURU NEPAL
NEPAL NETHERLANDS
NETHERLANDS NETHERLANDS ANTILLES
NETHERLANDS ANTILLES NEW CALEDONIA
NEW CALEDONIA NEW ZEALAND
NEW ZEALAND NICARAGUA
NICARAGUA NIGER
NIGER NIGERIA
NIGERIA NIUE
NIUE NORTH MACEDONIA
NORTH MACEDONIA NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS
NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS NORWAY
NORWAY OMAN
OMAN PAKISTAN
PAKISTAN PALAU
PALAU PALESTINE, STATE OF
PALESTINE, STATE OF PANAMA
PANAMA PAPUA NEW GUINEA
PAPUA NEW GUINEA PARAGUAY
PARAGUAY PERU
PERU PHILIPPINES
PHILIPPINES PITCAIRN ISLANDS
PITCAIRN ISLANDS POLAND
POLAND PORTUGAL
PORTUGAL PUERTO RICO
PUERTO RICO QATAR
QATAR REUNION
REUNION ROMANIA
ROMANIA RUSSIA
RUSSIA RWANDA
RWANDA SAINT BARTHELEMY (BARTS)
SAINT BARTHELEMY (BARTS) SAINT HELENA
SAINT HELENA SAINT KITTS AND NEVIS
SAINT KITTS AND NEVIS SAINT LUCIA
SAINT LUCIA SAINT MARTIN (DUTCH)
SAINT MARTIN (DUTCH) SAINT MARTIN (FRENCH)
SAINT MARTIN (FRENCH) SAINT PIERRE AND MIQUELON
SAINT PIERRE AND MIQUELON SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES
SAINT VINCENT AND THE GRENADINES SAMOA
SAMOA SAN MARINO
SAN MARINO SAO TOME AND PRINCIPE
SAO TOME AND PRINCIPE SAUDI ARABIA
SAUDI ARABIA SENEGAL
SENEGAL SERBIA
SERBIA SEYCHELLES
SEYCHELLES SIERRA LEONE
SIERRA LEONE SINGAPORE
SINGAPORE SLOVAKIA
SLOVAKIA SLOVENIA
SLOVENIA SOLOMON ISLANDS
SOLOMON ISLANDS SOMALIA
SOMALIA SOUTH AFRICA
SOUTH AFRICA SOUTH SUDAN
SOUTH SUDAN SPAIN
SPAIN SRI LANKA
SRI LANKA SUDAN
SUDAN SURINAME
SURINAME SWAZILAND (ESWATINI)
SWAZILAND (ESWATINI) SWEDEN
SWEDEN SWITZERLAND
SWITZERLAND SYRIA
SYRIA TAIWAN
TAIWAN TAJIKISTAN
TAJIKISTAN TANZANIA
TANZANIA THAILAND
THAILAND TOGO
TOGO TOKELAU
TOKELAU TONGA
TONGA TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO
TRINIDAD AND TOBAGO TUNISIA
TUNISIA TURKEY (TURKIYE)
TURKEY (TURKIYE) TURKMENISTAN
TURKMENISTAN TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS
TURKS AND CAICOS ISLANDS TUVALU
TUVALU UGANDA
UGANDA UKRAINE
UKRAINE UNITED ARAB EMIRATES (UAE)
UNITED ARAB EMIRATES (UAE) UNITED KINGDOM (UK)
UNITED KINGDOM (UK) UNITED STATES OF AMERICA (USA)
UNITED STATES OF AMERICA (USA) URUGUAY
URUGUAY US VIRGIN ISLANDS
US VIRGIN ISLANDS UZBEKISTAN
UZBEKISTAN VANUATU
VANUATU VATICAN CITY (HOLY SEE)
VATICAN CITY (HOLY SEE) VENEZUELA
VENEZUELA VIETNAM
VIETNAM WALLIS AND FUTUNA
WALLIS AND FUTUNA YEMEN
YEMEN ZAMBIA
ZAMBIA ZIMBABWE
ZIMBABWE